Good Sitting Posture | Health Benefits to Your Back

Many of us spend a significant amount of our day seated poorly, whether it be during commuting, office work, or leisure activities at home. Extended periods of lousy sitting can lead to health effects, like balance issues, reduced flexibility, etc. So, maintaining proper sitting posture is crucial.
Happily, good sitting position is achievable through consistent effort, mindfulness, and dedication. Good sitting habits play a significant role in up-keeping overall well-being and preventing many health issues.
This article explores the concept of good posture, describes the proper sitting position. Also, you will learn 11 tips to maintain a proper sitting habits at the desk. Keep reading!
Types of Sitting Posture

Let’s learn the types sitting postures, from cross-legged to balance position to improve comfort and well-being.
1. Cross-Legged Sitting
Cross-legged position involves sitting on the floor with legs crossed. This posture promotes flexibility and is commonly used in informal settings or meditation practices.
It can ease tension in the lower back but may become uncomfortable over extended periods.
2. Half-Lotus Sitting
In half-lotus position, one foot is placed on the opposite thigh while the other rests on the floor. It aids in spinal alignment and mindfulness. Regular practice enhances hip flexibility. However, it may strain the knees for some individuals.
3. Full Lotus Sitting
Full lotus position involves crossing both legs and placing each foot on the opposite thigh. Common in meditation, it demands flexibility and promotes an upright spine. But, beginners might find it challenging due to its advanced nature.
4. Kneeling Sitting
Kneeling sitting involves resting on the knees with the buttocks on the heels. It's suitable for short durations and comfortable on the lower back. However, it may lead to knee and ankle discomfort over time.
5. Chair Sitting
Chair sitting is the conventional way of sitting on a chair with feet flat on the floor. It provides back support and is suitable for various settings.
Though prolonged periods can contribute to poor posture and back issues if the chair lacks ergonomic design.
6. Reclined Sitting
In reclined position, the body leans back at an angle, distributing weight evenly. This posture is comfortable for relaxation. Bear in mind, it may not be ideal for activities requiring focus or an upright posture.
7. Perching Sitting
Perching means sitting on the edge of a surface with the feet on the ground. It encourages an active posture but can lead to discomfort over time.
This is commonly seen in dynamic work environments or situations requiring quick movement.
8. Side Sitting
Side sitting involves positioning on one side with legs bent. It's a relaxed posture suitable for casual settings. However, it might not provide adequate back support and may lead to discomfort during prolonged periods.
9. Saddle Sitting
Saddle position includes straddling a seat, similar to sitting on a horse saddle. It promotes an open hip angle and can reduce lower back strain. Commonly used in ergonomic chairs. It may take time to adapt to for some individuals.
10. Balanced Sitting
Balanced sitting emphasizes maintaining a neutral spine with feet flat on the ground. It's a versatile posture suitable for various activities, providing stability and comfort.
Regular breaks are essential to prevent stiffness during extended periods of balanced sitting.
Proper Sitting Posture

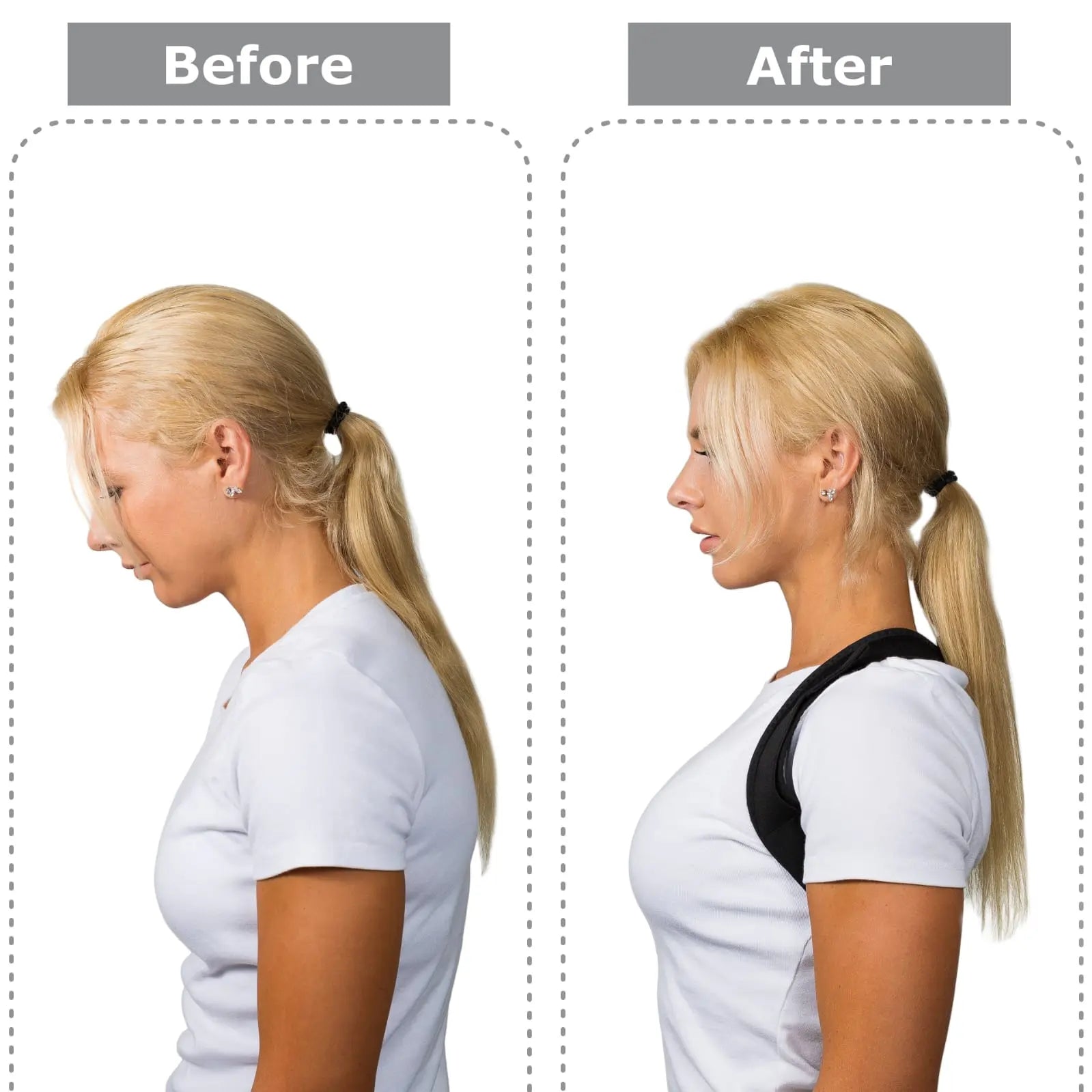
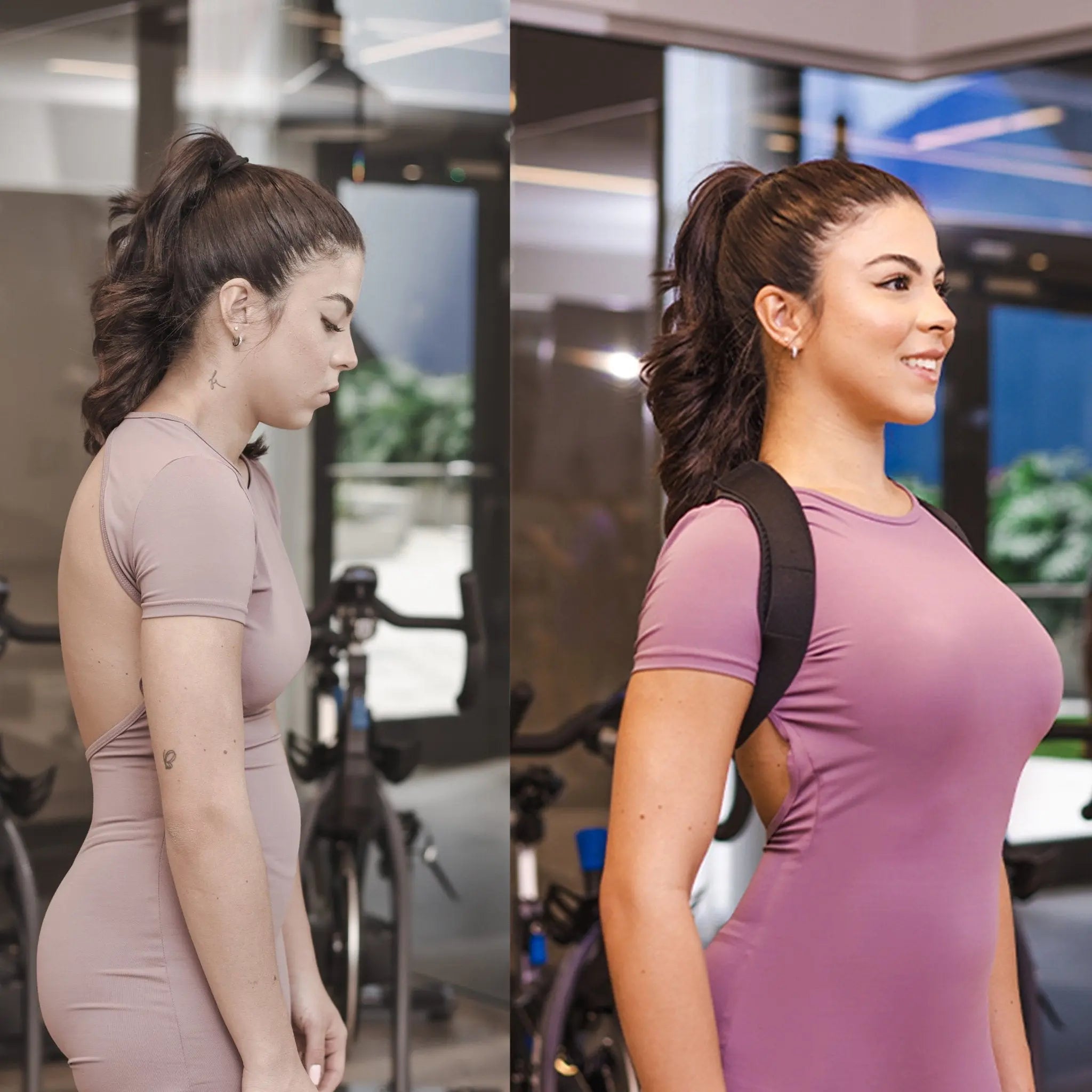
proper sitting posture is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of the musculoskeletal system. It minimizes strain on muscles and joints. Achieving an optimal position involves mindful alignment of various body parts.
Incorporating the below points into your habits can promote proper alignment. Also, consistent awareness of sitting habits and making adjustments as needed will contribute to a healthier and comfortable experience.
Here are key elements to consider for maintaining proper sitting posture:
- Align Your Head and Neck: Ensure your head is in a neutral position, directly above your shoulders. Avoid leaning forward or tilting your head excessively, as this can strain the neck and upper back.
- Position Your Shoulders: Keep your shoulders relaxed and in a natural position. Avoid hunching or rounding your shoulders forward, as this can lead to tension in the neck and upper back muscles.
- Elbows and Arms: Maintain a relaxed posture by keeping your elbows close to your body and forming an angle between 90° and 120°. This minimizes strain on the shoulders and prevents discomfort in the arms.
- Wrist and Hands: Keep your wrists neutral, helping you avoid excessive bending or extension. Your hands should comfortably rest on the desk or keyboard for easy movement.
- Back Support: Use a chair with proper lumbar support to maintain the natural curve of your spine. Ensure that your back is straight. Also, your lower back should adequately be supported to prevent slouching or arching.
- Hip Position: Position your hips at the back of the chair, allowing them slightly higher than your knees. This promotes a proper pelvic tilt and helps maintain the spine's natural curvature.
- Knee Angle: Maintain a 90-degree angle at the knees, with your feet flat on the floor. Use a footrest to support your feet and avoid crossing your legs. Otherwise, it can hinder proper blood circulation.
- Feet Placement: Place your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. This provides a stable base and prevents unnecessary pressure on the lower back. Avoid dangling your feet or sitting on them, as this can lead to discomfort.
- Distribution of Weight: Distribute your body weight evenly on both hips. This prevents excess pressure on one side of the body, reducing the risk of developing imbalances and discomfort.
- Breaks and Movement: Take regular breaks to stand, stretch, and move around. Prolonged sitting can lead to stiffness and muscle fatigue. Follow simple stretches and movements into your routine to maintain flexibility.
Proper Sitting Posture at a Computer Desk – 11 Tips

“Back pain occurs when you don’t sit properly at your desk”, says Dr. Gary Allread, PhD, CPE, program director for SRI Ergonomics at the Ohio State Spine Research Institute
Discover 11 essential tips for maintaining proper sitting posture at your computer desk. From chair adjustments to ergonomic accessories, enhance comfort, productivity, and overall well-being in your workspace.
Proper Sitting Posture Tips and Mistakes to Avoid
1. Chair Height
- Tip: Keep your feet flat on the floor by adjusting the chair height. Also, have your knees at a 90° angle.
- Mistake to Avoid: Don’t sit with your feet dangling or unable to touch the floor.
2. Chair Support
- Tip: Maintain the natural curve of your spine by using the chair's lumbar support to.
- Mistake to Avoid: Don’t avoid the lumbar support. It can lead to slouching and poor spinal alignment.
3. Keyboard and Mouse Placement
- Tip: Position your keyboard and mouse at a height that allows your elbows to form a 90° angle.
- Mistake to Avoid: Placing the keyboard and mouse too high or too low causes strain on the wrists and arms.
4. Monitor Position
- Tip: Set your monitor at eye level to reduce strain on your neck and avoid tilting your head.
- Mistake to Avoid: Having the monitor too high or too low leads to neck and eye discomfort.
5. Posture Check
- Tip: Periodically assess your posture, ensuring your back is straight and shoulders are relaxed.
- Mistake to Avoid: Slouching or leaning forward for extended periods without regular posture checks.
6. Breaks and Movement
- Tip: Take short breaks to stand, stretch, and move around every 30 minutes.
- Mistake to Avoid: Sitting for prolonged periods without breaks contributes to stiffness and discomfort.
7. Eye Level
- Tip: Keep your eyes level with the top third of the screen to reduce strain on your neck and eyes.
- Mistake to Avoid: Tilting your head up or down excessively while viewing the screen.
8. Armrests
- Tip: Adjust armrests to support your arms comfortably, preventing shoulder and neck tension.
- Mistake to Avoid: Having armrests too high or too low leads to discomfort and poor arm support.
9. Feet Placement
- Tip: Place your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart, to provide a stable base and support your lower back.
- Mistake to Avoid: Crossing your legs or allowing your feet to dangle, causing discomfort and poor weight distribution.
10. Desk Organization
- Tip: Organize your desk essentials within easy reach to minimize excessive reaching or twisting.
- Mistake to Avoid: Cluttering your desk or placing items too far away, leading to awkward postures and strain.
11. Use Ergonomic Accessories
- Tip: Invest in ergonomic accessories such as a chair, keyboard, or mouse to enhance comfort and support.
- Mistake to Avoid: Using non-ergonomic accessories that contribute to discomfort and poor posture.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does it hurt to sit up straight?
It is not in keeping with nature for our spine to be rigid. Rather, it should have a few gentle curves. Many folks will tell you to sit up straight, but if you do, you're putting extra strain on your spine.
Which chair is best for posture?
Saddle chairs encourage healthier spinal postures, especially in the upper back, neck, and head. The academic evidence backs the claim that these chairs have low accident risk even when compared with traditional chairs.
Why can't I sit in a chair normally?
When you combine bad posture with extended periods of sitting, you're likely to experience discomfort. Sitting is bad for our health because it restricts blood flow, traps nerves, and wastes muscle. When you sit for too long, your body has to work harder.
Why can't I sit up straight?
There could be a number of factors at play if you're having trouble maintaining an erect posture. There's a chance that your hip flexors are not flexible.
To add to that, your lower back might not be tucked up enough. As a third possibility, you might be keeping your back straight by contracting your abdominal muscles.
Where should lumbar support be on your back?
It's best to position the lumbar support where your spine naturally curves. The majority of chairs have this feature integrated into the design. It allows the user to alter the height of the backrest and the lumbar support simultaneously.
When sitting in a chair is it important to maintain posture?
Yes, it is important to maintain posture because it stimulates your muscles, ligaments, and tendons and helps maintain healthy blood flow, nerves, and blood vessels.
Wrapping Up
Maintaining a proper sitting posture is vital to minimizing the risk of chronic diseases and enhancing overall health.
Adequate sitting position reduces back pain and enhances blood circulation, increasing productivity during extended work sessions. Achieving good habits are valuable for long-term health benefits.