How To Fix Flat Back Posture? Suggestions For A Speedy Cure

Flatback syndrome (FBS) is a spinal condition characterized by the loss of the natural curvature in the lumbar spine. As a result, you will have a flattened back. Such imbalances affect posture, causing difficulties in standing and walking.
Moreover, you will face discomfort while accomplishing your daily activities. Also, sensation of falling forward is a symptom of flatback. Early intervention, including non-surgical approaches like physical therapy is essential to prevent this syndrome.
Let’s begin our discussion about the symptoms, causes, and diagnosis process of FBS. We shared step-by-step guides of a few exercises regarding how to fix flat back posture.
What is Flat Back Syndrome?

Flatback syndrome (FBS) is a sagittal imbalance that affects the lower spine, specifically the lumbar region. It leads to the loss of its natural curvature over time.
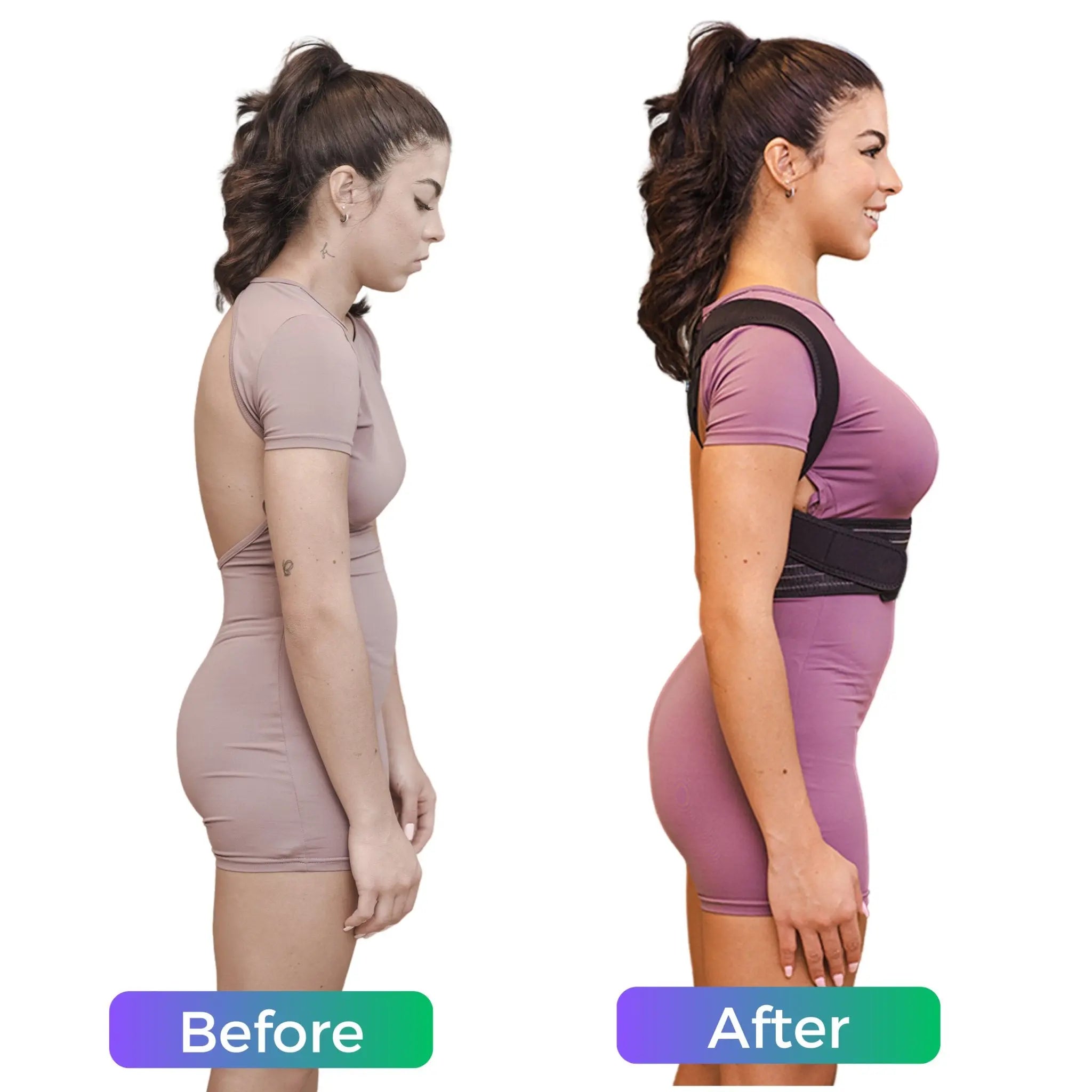
This condition is characterized by decreased lordosis, letting individuals to lean forward. As a result, you will face difficulty to stand upright and walk efficiently.
In return of the flat lumbar spine, the rest of the spine adopts strategies like forward head posture, pelvic tilting, and flexion in the hips and knees.
These compensatory mechanisms are causing muscle fatigue and pain. Moreover, it gives the body a pitched-forward appearance. Thus, it becomes a challenge to maintain a straight and balanced posture.
Symptoms of Flatback Posture

Common symptoms are physical discomfort, a gradual decline in the ability to perform daily activities, etc. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial to minimize the symptoms.
1. Lower Back Pain
One of the primary symptoms of Flat Back Syndrome (FBS) is lower back pain. As the lumbar spine loses its natural curvature, it creates stress on the muscles, ligaments, and joints in the lower back.
This persistent strain often causes aching pain. Over time, the discomfort may intensify and become chronic.
2. Stiffness
People with flatback often experience lower back and hips stiffness. The altered alignment of the spine limits the normal range of motion. It leads to stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity.
Such a stiffness can further contribute to discomfort. Also, performing everyday tasks, such as bending or twisting becomes difficult.
3. Difficulty Standing Upright
Flat Back Syndrome causes an imbalance in the spine. This way, you may lean forward while standing or sitting. This forward-leaning posture makes it challenging to stand upright.
Generally, we may adopt forward-leaning positions to maintain balance, causing strain on the muscles and joints. The constant effort to counteract the spinal imbalance can result in muscle fatigue.
4. Impaired Balance
The loss of the natural lumbar curvature disrupts the body's balance mechanisms. Individuals with FBS struggle to maintain an upright posture. So, their overall balance is compromised.
Such an impaired balance increases the risk of falls. It also contributes to a sense of instability, impacting daily activities such as walking and climbing stairs. Overall, the altered biomechanics causing leading to movement difficulties.
5. Quality of Life Impact
Flatback syndrome can significantly reduce the quality of your life. You will fail to perform routine activities due to lower back pain, stiffness, difficulty standing upright.
Moreover, simple tasks like walking, standing for extended periods, or sitting comfortably may become arduous. If left untreated, flat back syndrome can lead to emotional distress, potentially leading to issues such as anxiety and depression.
Causes of Flat Back Syndrome

Flat back syndrome can arise from various factors, each contributing to the loss of the natural curvature in the lumbar spine. Understanding the diverse causes is essential for effective diagnosis and targeted treatment.
1. Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease commonly contributes to FBS. As intervertebral discs wear down over time, they lose their ability to provide proper support. This degeneration can lead to a reduction in the lumbar lordosis, resulting in a flattened spine.
2. Spinal Fusion Surgery
Flat-back syndrome can be an unintended consequence of spinal fusion surgery. The fusion aims to stabilize the spine. It can inadvertently alter the natural curvature, causing a loss of lordosis.
The fused segments become rigid, potentially impacting adjacent spinal levels and leading to a flat-back deformity.
3. Muscle Imbalances
Imbalances in the muscles supporting the spine can play a significant role in developing flat back. Weakness or tightness in the muscle groups of lumbar and pelvic region can contribute to the flattening of the spine.
4. Poor Posture and Prolonged Sitting
Modern sedentary lifestyles often involve extended hours spent sitting. It leads to weakened core muscles and increased stress on the lumbar spine. Over time, this can result in the loss of lumbar lordosis, developing FBS.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain underlying medical conditions can predispose individuals to Flat Back Syndrome. Ankylosing spondylitis, a form of inflammatory arthritis affecting the spine, causing fusion of vertebral joints.
This fusion, coupled with inflammation and structural changes. Then, contributing to a flattened spine characteristic of Flat Back Syndrome.
Diagnosis of Flat Back Syndrome

An accurate diagnosis is crucial for an effective treatment plan according to the patient's specific needs.
1. Physical Examination
The diagnostic process for Flat Back Syndrome typically begins with a thorough physical examination. The healthcare provider assesses the patient's posture, gait, and overall alignment during this examination. They observe how the individual stands, walks, and performs specific movements.
2. Medical History Review
A comprehensive review of the patient's medical history is crucial. Gathering information about past spinal surgeries, existing medical conditions, etc. Helps professionals understand the potential contributing factors of flat back syndrome.
3. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are often used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of spinal deformity. X-rays provide detailed spine images, allowing professionals to visualize the curvature and alignment.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may assess soft tissues, discs, and potential nerve impingements. These imaging modalities help identify structural abnormalities.
4. Assessment of Curvature
Healthcare professionals use various radiographic measurements to assess the curvature of the spine.
The lumbar lordosis angle, which represents the natural curvature of the lower spine, is a crucial parameter. Deviations from the standard range indicate the presence of a flat-back deformity.
Flat Back Syndrome Exercises
Consistency in performing these exercises can contribute to improved posture and increased strength in the muscles supporting the spine, benefiting individuals with Flat Back Syndrome.
1. Pelvic Tilt
Strengthen and mobilize the lower back and pelvis with the pelvic tilt exercise.
- Step 01: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor.
- Step 02: Inhale and tilt your pelvis backward, pressing your lower back into the floor.
- Step 03: Exhale and tilt your pelvis forward, arching your lower back slightly.
- Step 04: Repeat this rocking motion.
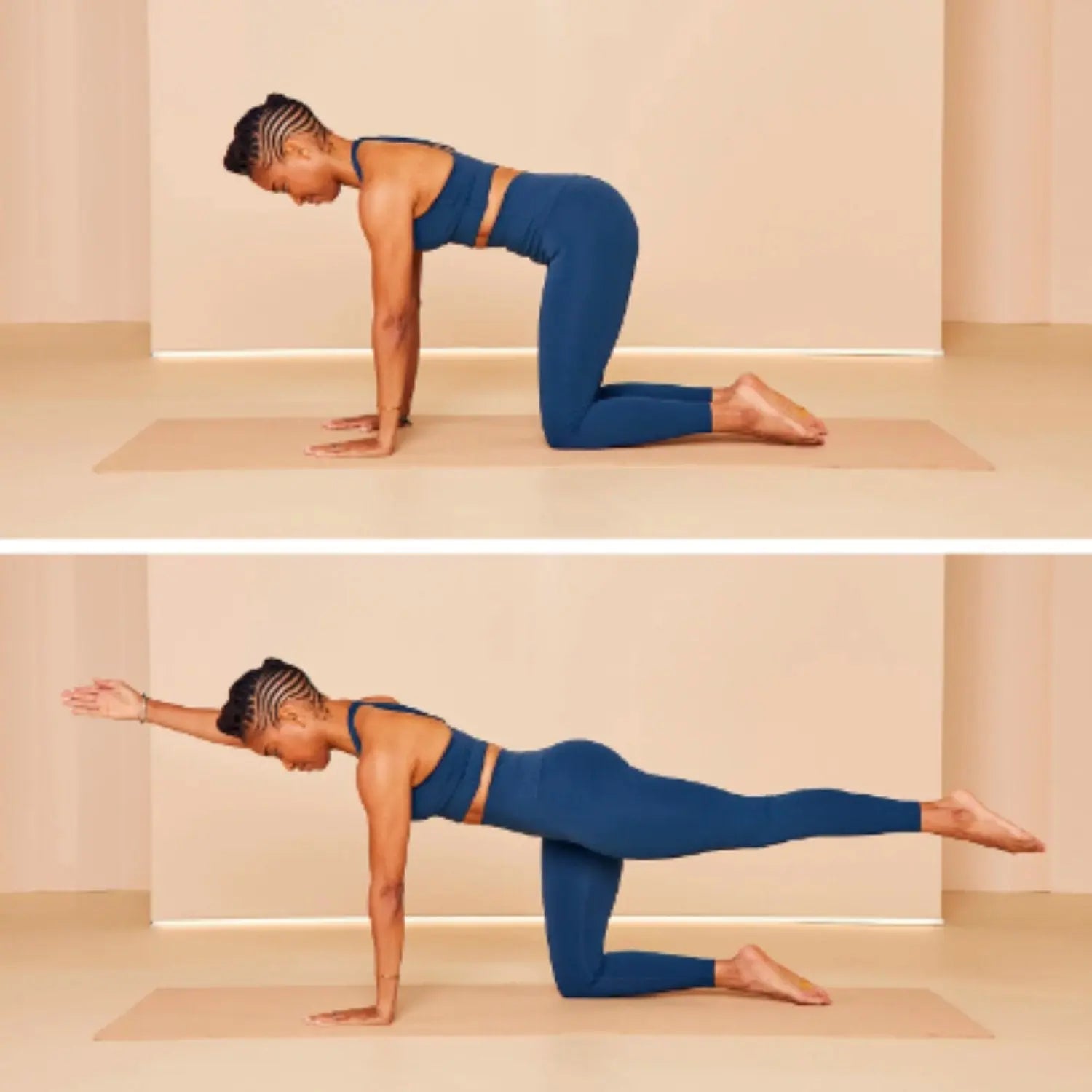
2. Cat-Cow Stretch

Cat-cow stretch helps you improve flexibility and mobility in the spine.
- Step 01: Start on your hands and knees in a tabletop position.
- Step 02: Inhale, arch your back and lift your head and tailbone (Cow).
- Step 03: Exhale, round your spine, and tuck your chin to your chest (Cat).
- Step 04: Repeat this fluid motion.
3. Superman Exercise
Strengthen the back extensors with the help of superman exercise.
- Step 01: Lie on your stomach with your arms extended in front.
- Step 02: Lift your arms, chest, and legs off the floor simultaneously, squeezing your glutes and lower back muscles.
- Step 03: Hold for a few seconds, then lower back down.
- Step 04: Repeat
4. Bridge Exercise
Bridge exercise will let you target the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back.
- Step 01: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet hip-width apart.
- Step 02: Lift your hips toward the ceiling, forming a straight line from shoulders to knees.
- Step 03: Squeeze your glutes at the top, then lower back down.
- Step 04: Repeat
5. Plank

Plank is an ideal exercise for strengthening the core, back, and shoulders.
- Step 01: Start in a plank position with hands beneath shoulders.
- Step 02: Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels.
- Step 03: Engage your core and hold the position, avoiding sagging or lifting the hips.
- Step 04: Start with shorter durations and gradually increase over time.
6. Seated Leg Lifts
Engage the hip flexors and core with seated leg lifts.
- Step 01: Sit on the edge of a chair with feet flat on the floor.
- Step 02: Lift one leg straight out in front, hold briefly, then lower—alternate legs.
- Step 03: Keep your back straight and engage your core.
7. Child's Pose

Child’s pose will help stretching and relaxing the lower back.
- Step 01: Kneel on the floor with toes together and knees apart.
- Step 02: Sit back on your heels, reaching your arms forward.
- Step 03: Lower your chest toward the floor, stretching your arms and elongating the spine.
- Step 04: Hold and breathe deeply.
8. Wall Angels
Improve posture and shoulder mobility by doing wall angles exercise.
- Step 01: Stand with your back against a wall.
- Step 02: Raise your arms overhead, keeping them in contact with the wall.
- Step 03: Lower your arms, bending at the elbows to create "angel wings."
- Step 04: Repeat while maintaining contact with the wall.
Medical Interventions and Treatments for Flat Back Syndrome
There are a range of medical interventions exist for individuals with flatback, addressing both non-surgical and surgical options.
“Non-surgical treatment for Flatback includes physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications”, says Dr. Samuel Bederman.
Non-Surgical Interventions
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and stretches can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and spinal alignment.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors may employ spinal adjustments to enhance vertebral alignment and alleviate symptoms.
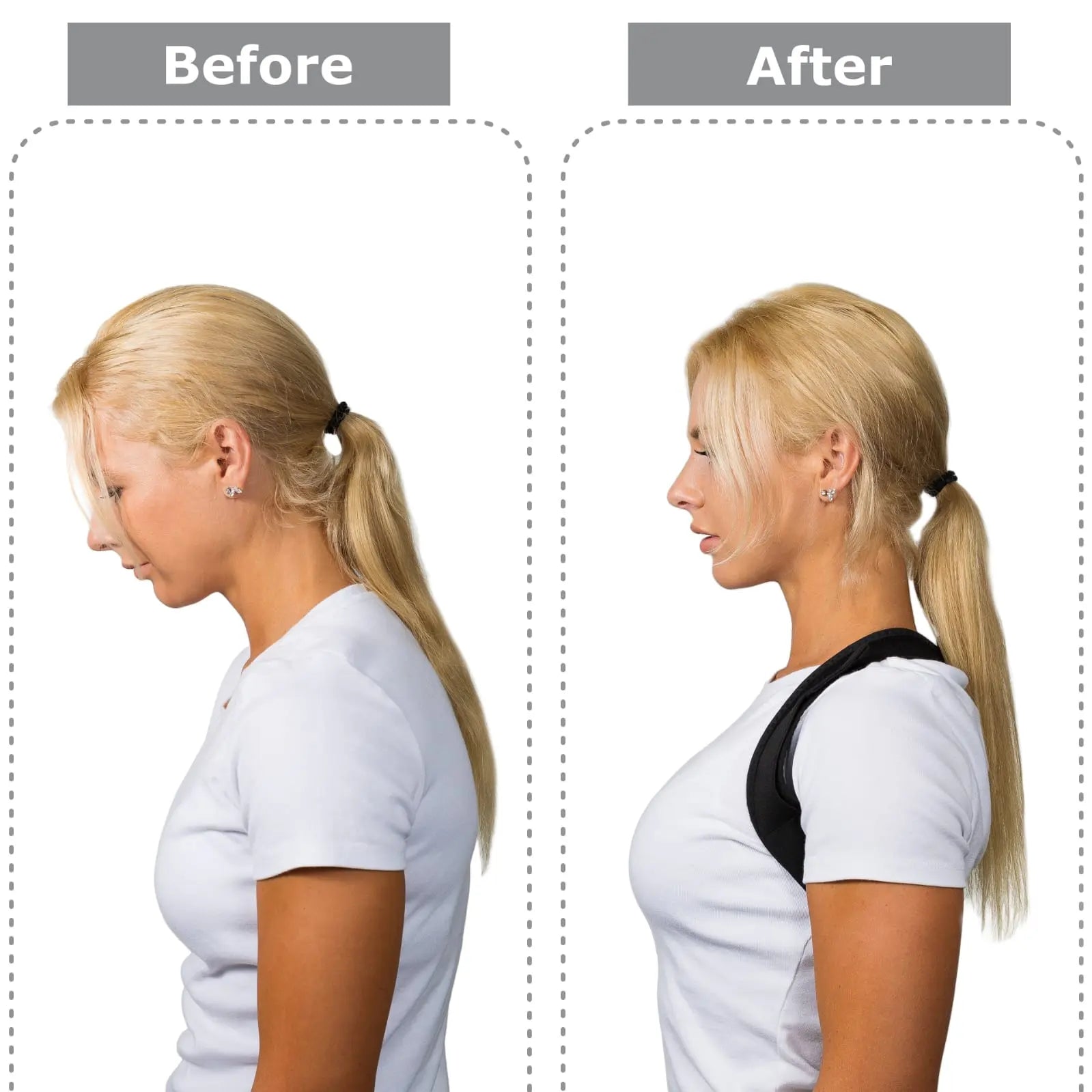
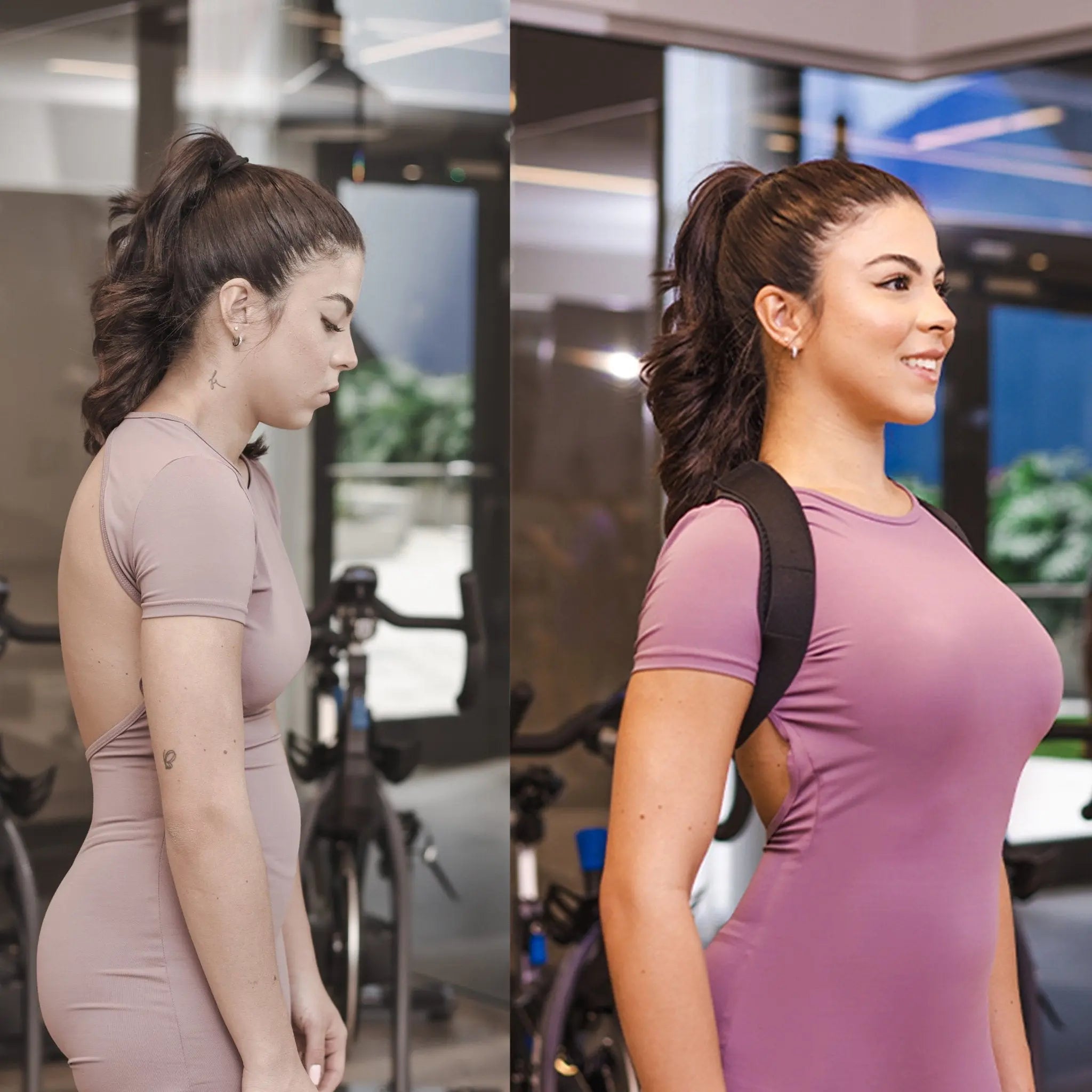
- Postural Braces: Postural Braces can provide external support, aiding in maintaining a more natural spinal curvature and preventing further deformity.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Interventions
- Spinal Fusion: In severe cases, spinal fusion surgery may be recommended. This procedure involves connecting two or more vertebrae to restrict movement, stabilizing the spine.
- Osteotomy: This surgical intervention entails removing a wedge of bone to correct spinal alignment and restore a more natural curvature.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can flat back be corrected?
Flat-back posture can be cured through exercises targeting the weakened neck, back, and core muscles.
Studies show that combining corrective exercises for the thoracolumbar spine with other strengthening exercises can treat muscle imbalances over time.
Why is my lower back flat?
Flatback syndrome can occur for multiple reasons, but the most common one is a degenerative disc in the lumbar region.
Other factors may include vertebral compression fractures due to osteoporosis or arthritis; which contribute to the weakening of the spine and make the back flat.
What muscles cause flat back posture?
The muscles that are responsible for flat back posture are usually the erector spinae in the lumbar region, which maintain the natural curvature of the back.
Weakness in hip flexors such as the illacus and rectus femoris can be the reason behind this posture.
What muscles are weak in a flat back?
The neck, lower back, and core muscles get highly affected due to a flat back. Core muscles like the transversus abdominis, muscles in the lumbar region, and gluteus muscles weaken and cause severe pain and discomfort.
Wrapping Up
Early intervention can help fix flat black posture, and improve spinal function. By following the above-mentioned exercises, solving flatback syndrome will be straightforward.
However, consulting a healthcare professional is always vital. A collaborative approach between the consultant and patient makes the fixing process effective. So, whenever you experience FBS, consult your doctor and take necessary steps.